Pakistan's economy has been grappling with significant challenges, particularly in relation to the volatility of its currency, the Pakistani Rupee. This article delves into the underlying factors contributing to the rupee's volatility, including capital inflows, currency crises, fiscal spending, inflationary pressures, and the broader economic landscape in Pakistan. The Observer Research Foundation (ORF) offers insights into the complexities of Pakistan's currency fluctuations and examines potential strategies to mitigate the negative effects on the economy.

Capital Inflows and Currency Crises:
Fluctuations in the Pakistani Rupee are often influenced by capital inflows, both foreign investments and remittances from overseas Pakistanis. These inflows can have a significant impact on the exchange rate, as they affect the supply and demand dynamics of the currency. However, sudden reversals or uncertainties in capital flows can trigger currency crises, leading to sharp depreciation of the rupee. The ORF highlights the importance of managing capital inflows effectively to ensure stability in the currency market.
Fiscal Spending and its Impact:
Fiscal spending policies play a crucial role in shaping the currency's stability. Excessive government expenditure, particularly if not backed by adequate revenue generation or foreign reserves, can put immense pressure on the currency. Large fiscal deficits, coupled with a lack of fiscal discipline, can erode investor confidence and lead to currency depreciation. The ORF emphasizes the need for prudent fiscal management and structural reforms to address fiscal imbalances and mitigate currency volatility.
Inflationary Pressures and their Influence:
Inflationary pressures also contribute significantly to the rupee's volatility. Persistent inflation erodes the purchasing power of the currency, leading to depreciation. Factors such as rising commodity prices, energy costs, and monetary policy decisions impact inflation levels. The ORF emphasizes the importance of adopting effective inflation management policies, including maintaining price stability and implementing measures to control inflationary pressures, to foster currency stability.
Navigating Pakistan's Economic Landscape:
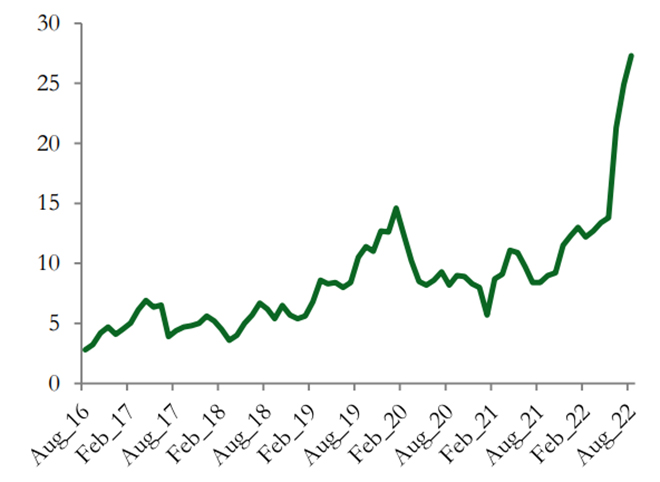
Pakistan's economic landscape, including its external trade balance, foreign reserves, and debt dynamics, plays a crucial role in determining the rupee's trajectory. Structural reforms, attracting foreign investments, enhancing export competitiveness, and reducing reliance on external borrowing are essential to strengthen the economy and stabilize the currency. The ORF advocates for comprehensive economic reforms aimed at enhancing productivity, diversifying exports, and improving the business environment.
Mitigating the Negative Effects:
To mitigate the negative effects of rupee volatility, the ORF suggests several measures. These include maintaining a robust foreign exchange reserve position, implementing prudent monetary policies, encouraging foreign investments, promoting export-oriented industries, and fostering a transparent and predictable business environment. Additionally, enhancing financial literacy and investor awareness can help individuals and businesses better navigate the challenges posed by currency fluctuations.
Conclusion:
Pakistan's rupee volatility poses significant challenges to its economy, affecting businesses, investors, and the general public. Addressing the root causes of volatility, such as capital inflows, fiscal spending, inflationary pressures, and broader economic factors, is crucial for ensuring currency stability. The Observer Research Foundation (ORF) highlights the importance of prudent fiscal management, structural reforms, and effective economic policies to mitigate the negative effects of rupee depreciation. By adopting a comprehensive approach and implementing sound strategies, Pakistan can work towards a more stable currency and a resilient economy.






